Clinical evidence
A prospective single-arm, single-centre first in human study
to collect data on usability and confirm safety of SmartPAN
has been conducted.
Preclinical evidence
The safety and efficacy of SmartPAN has been evaluated
both in vivo and in vitro.
PMCF study.
Introduction
- Postoperative pancreatic fistula (POPF) is the most serious complication of pancreatic surgery. The SmartPAN® indicator was developed for
intraoperative visualization of pancreatic leaks. This is intended to predict POPF development and enable targeted closure.
Objectives
- The ViP study represents the first stage in the clinical phase according to IDEAL guidelines for surgical innovation. The objective was to investigate the
clinical utility and confirm the safety of The SmartPAN® application in pancreatic surgery.
Methodology
- This was a prospective, single-arm, exploratory clinical trial. A total of 42 patients with indication for elective partial pancreatectomy were included.
Analyzed were usefulness based on adherence to the study protocol and surgeon assessment, as well as safety including relevant complications
(Clavien-Dindo classification, CDC grade III-V) and their association with SmartPAN® use. The analysis focused on specific pancreatic surgical
complications reoperation rates and non-surgical interventions.
Results
- 30 patients were analyzed: 11 distal pancreatectomies (DP, 37%), 9 partial pancreaticoduodenectomies (PD, 30%), 33% multivisceral resections (6 DP, 4
DP), 20% of which were minimally invasive. Indicator response was negative in 20 surgeries. All 6 indicator-positive DPs received targeted closure, but
only 3 of 4 indicator-positive PDs. - One study protocol violation (3.3%) with inappropriate indicator use was excluded from the complication analysis.
- Indicator response always happened within 3 minutes (60% within <30 seconds), with 70% of surgeons rating the response as “accurate” and 90% as
“durable.” 100% of surgeons reported that the indicator was “easy to use,” 89.3% that it was “useful for my work,” and 93.3% would “like to use it
frequently.” - No complications occurred during surgery, 27.6% of patients experienced a pancreas-specific complication CDC grade ≥3a or CT-guided drain insertion,
10.3% underwent reoperation, and 30-day mortality was 10%, with deaths occurring after surgery including vascular resections. No causal association
with SmartPAN® use was identified, and overall mortality and morbidity were comparable to historical internal RCT data. The rate of clinically relevant
POPF was 20% in indicator-negative PDs and 16.7% after targeted closure.
Conclusion
- The ViP study confirms the safety of the SmartPAN® indicator and shows its usefulness in pancreatic surgery. It provides the basis for multicenter
randomized controlled intervention studies.
Abstract IDEAL Stage I Clinical Study Confirms the utility and safety of visualizing pancreatic leaks with SmartPAN® indicator
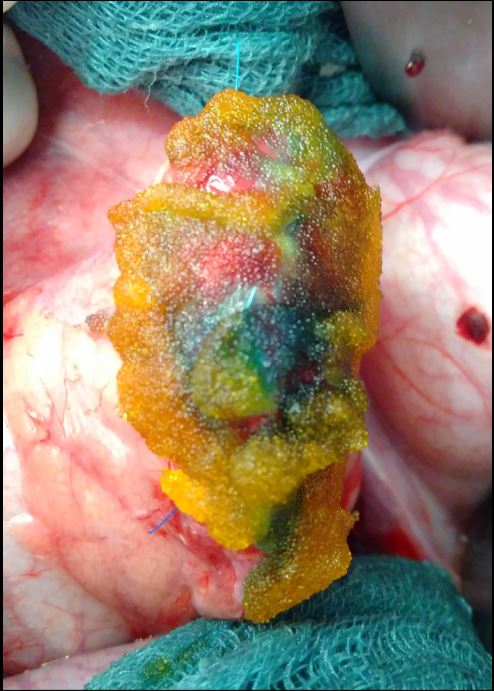
Introduction
- Postoperative pancreatic fistula (POPF) is the most serious complication of pancreatic surgery. The SmartPAN® indicator was developed for intraoperative
visualization of pancreatic leaks. This is intended to predict POPF development and enable targeted closure.
Objectives
- The ViP study represents the first stage of the clinical phase according to IDEAL guidelines for surgical innovation. The aim was to investigate clinical usability
and confirm safety.
Methodology
- This was a prospective, single-arm, exploratory clinical study. A total of 42 patients with an indication for elective partial pancreatectomy were included. The
usability was analyzed based on compliance with the study protocol and the surgeon’s assessment as well as the safety including relevant complications
(Clavien-Dindo grade III-V) and their connection to the SmartPAN® application. The focus of the analysis was on pancreatic surgery complications,
reoperation rates and non-surgical interventions.
Results
- 30 patients were analyzed: 11 distal pancreatectomies (DP, 37%), 9 partial pancreaticoduodenectomies (PD, 30%), 33% multivisceral resections (6 DP, 4DP),
20% of them minimally invasive. In 20 operations the indicator reaction was negative. All 6 indicator-positive DPs were selectively closed, but only 3 of 4
indicator-positive PDs were closed. - One (3.3%) protocol violation involving inappropriate use was excluded from complication analysis. The reaction always occurred within 3 minutes (60% in
<30 seconds). 100% of surgeons said the indicator was “easy to use,” 89.3% said it was “useful for my work,” and 93.3% said they would “like to use it
frequently.” In 27.6% of patients there was a postoperative complication CDC°=3a, 10.3% were re-operated and the 30-day mortality was 10%. No causal
relationship with SmartPAN® use could be established, and all-cause mortality and morbidity were comparable to historical internal RCT data. The rate of
clinically relevant POPF was 20% in indicator-negative PDs and 16.7% after targeted closure in PDs.
Conclusion
- The ViP study confirms the safety of the SmartPAN® indicator and its usefulness in pancreatic surgery. It provides the basis for multicenter randomized controlled intervention studies.